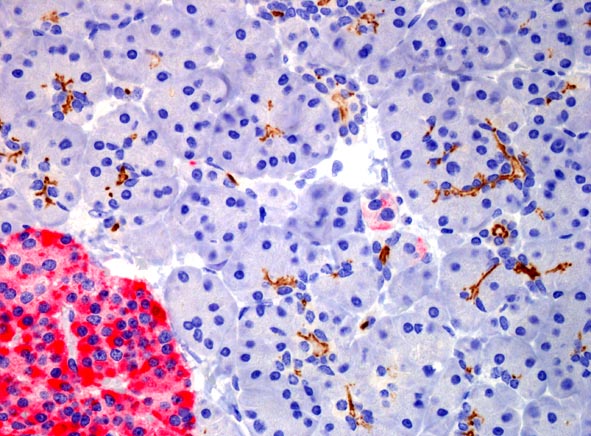
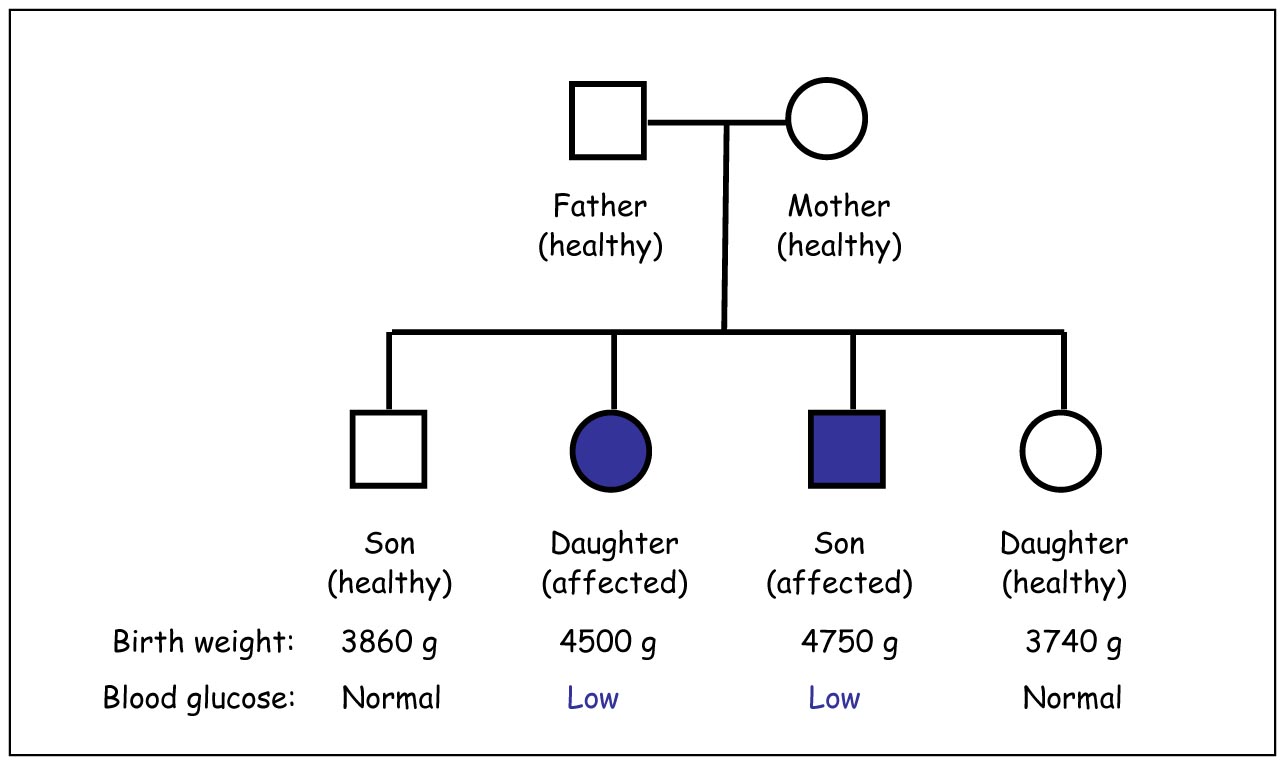
Diabetes can be divided into several subtypes. The two most common are type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In some cases, the disease is inherited as a monogenic disorder denoted “maturity-onset diabetes of the young” (MODY), of which there are at least ten variants. We are studying Norwegian MODY families with the aim to identify their mutations and to understand the biological effects of the affected proteins by performing functional analyses. Examples of our research results are our discoveries that mutations in the insulin gene (INS) can cause MODY and that disturbed insulin signaling may lead to a syndrome of lipodystrophy, short stature and insulin resistance. We have a special interest in MODY8, the MODY type caused by mutations in the carboxyl ester lipase (CEL) gene.
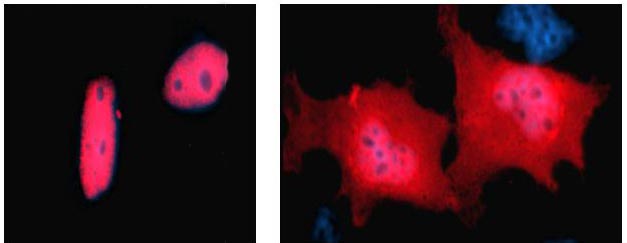
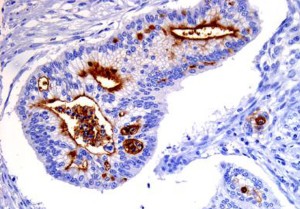
Cells with normal (left) and mutant (right) HNF1-alpha protein, which causes MODY3 or
HNF1A-MODY. Normally, the protein is present in the nucleus only. The mutant form
accumulates in the cytoplasm.
Participants / collaborators
About 30 persons at the University of Bergen and Haukeland University Hospital participate in this research effort, which is lead by profs. Pål R. Njølstad and Stefan Johansson at the Section for Pediatrics, Department of Clinical Science. The projects involve extensive international collaboration and were performed under the auspices of the KG Jebsen Center for Diabetes Research (2012-2018), which now is continued as the Bergen Center for Diabetes Research.
Publications
Gravdal A, Wilhelm SJ; CEL-MODY Mouse Project; Lowe ME, Molven A, Xiao XK & Fjeld K. (2025). The MODY-causing mutation of the human carboxyl ester lipase gene (CEL) triggers chronic pancreatitis but not diabetes in mice. Gastroenterology (in press).
Svalastoga P, Kaci A, Molnes J, Solheim MH, Johansson BB, Krogvold L, Skrivarhaug T, Valen E, Johansson S, Molven A, Sagen JV, Søfteland E, Bjørkhaug L, Tjora E, Aukrust I & Njølstad PR (2023). Characterization of HNF1A variants in paediatric diabetes in Norway using functional and clinical investigations to unmask phenotype and monogenic diabetes. Diabetologia 66: 2226-2237.
El Jellas K, Dušátková P, Haldorsen IS, Molnes J, Tjora E, Johansson BB, Fjeld K, Johansson S, Průhová Š, Groop L, Löhr J-M, Pål R. Njølstad PR & Molven A (2022). Two new mutations in the CEL gene causing diabetes and hereditary pancreatitis: How to correctly identify MODY8 cases. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 107: e1455-1466.
Althari A, Najmi LA, Bennett AJ, Aukrust I, Rundle JK, Colclough K, Molnes J, Kaci A, Nawaz S, van der Lugt T, Hassanali N, Mahajan A, Molven A, Ellard S, McCarthy MI, Bjørkhaug L, Njølstad PR & Gloyn AL (2020). Unsupervised clustering of missense variants in HNF1A using multidimensional functional data aids clinical interpretation. American Journal of Human Genetics 107: 670-682.
Helgeland Ø, Vaudel M, Júlíusson PB, Holmen OL, Juodakis J, Bacelis J, Jacobsson B, Lindekleiv H, Hveem K, Lie RT, Knudsen GP, Stoltenberg C, Magnus P, Sagen JV, Molven A, Johansson S & Njølstad PR (2019). Genome-wide association study reveals dynamic role of genetic variation in infant and early childhood growth. Nature Communications 10: 4448.
Solheim MH, Winnay JN, Batista TM, Molven A, Njølstad PR & Kahn CR (2018). Mice carrying a dominant-negative human PI3K mutation are protected from obesity and hepatic steatosis but not diabetes. Diabetes 67: 1297-1309.
Sagen JV, Bjørkhaug L, Haukanes BI, Grevle L, Molnes J, Nedrebø BG, Søvik O, Njølstad PR, Johansson S & Molven A (2017). The HNF1A mutant Ala180Val: Clinical challenges in determining causality of a rare HNF1A variant in familial diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 133: 142-149.
Solheim MH, Clermont AC, Winnay JN, Hallstensen E, Molven A, Njølstad PR, Rødahl E & Kahn CR (2017). Iris malformation and anterior segment dysgenesis in mice and humans with a mutation in PI 3-kinase. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 58: 3100-3106.
Johansson BB, Irgens HU, Molnes J, Sztromwasser P, Aukrust I, Juliusson PB, Søvik O, Levy S, Skrivarhaug T, Joner G, Molven A, Johansson S & Njølstad PR (2017). Targeted next-generation sequencing reveals MODY in up to 6.5% of antibody-negative diabetes cases listed in the Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia 60: 625-635.
Najmi LA, Aukrust I, Flannick J, Molnes J, Burtt N, Molven A, Groop L, Altshuler D, Johansson S, Bjørkhaug L & Njølstad PR (2017). Functional investigations of HNF1A identify rare variants as risk factors for type 2 diabetes in the general population. Diabetes 66: 335-346.
Winnay JN, Solheim MH, Dirice E, Sakaguchi M, Noh HL, Kang HJ, Takahashi H, Chudasama KK, Kim JK, Molven A, Kahn CR & Njølstad PR (2016). PI3-kinase mutation linked to insulin and growth factor resistance in vivo. Journal of Clinical Investigation 126: 1401-1412
Irgens HU, Fjeld K, Johansson BB, Ringdal M, Immervoll H, Leh S, Søvik O, Johansson S, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2015). Glycogenin-2 is dispensable for liver glycogen synthesis and glucagon-stimulated glucose release. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 100: E767-775.
Helgeland Ø, Hertel JK, Molven A, Ræder H, Platou CG, Midthjell K, Hveem K, Nygård O, Njølstad PR & Johansson S (2015). The chromosome 9p21 CVD- and T2D-associated regions in a Norwegian population (the HUNT2 Survey). International Journal of Endocrinology 2015: 164652.
Flannick J, Thorleifsson G, Beer NL, Jacobs SB, Grarup N, Burtt NP, Mahajan A, Fuchsberger C, Atzmon G, Benediktsson R, Blangero J, Bowden DW, Brandslund I, Brosnan J, Burslem F, Chambers J, Cho YS, Christensen C, Douglas DA, Duggirala R, Dymek Z, Farjoun Y, Fennell T, Fontanillas P, Forsén T, Gabriel S, Glaser B, Gudbjartsson DF, Hanis C, Hansen T, Hreidarsson AB, Hveem K, Ingelsson E, Isomaa B, Johansson S, Jørgensen T, Jørgensen ME, Kathiresan S, Kong A, Kooner J, Kravic J, Laakso M, Lee JY, Lind L, Lindgren CM, Linneberg A, Masson G, Meitinger T, Mohlke KL, Molven A, Morris AP, Potluri S, Rauramaa R, Ribel-Madsen R, Richard AM, Rolph T, Salomaa V, Segrè AV, Skärstrand H, Steinthorsdottir V, Stringham HM, Sulem P, Tai ES, Teo YY, Teslovich T, Thorsteinsdottir U, Trimmer JK, Tuomi T, Tuomilehto J, Vaziri-Sani F, Voight BF, Wilson JG, Boehnke M, McCarthy MI, Njølstad PR, Pedersen O, Groop L, Cox DR, Stefansson K & Altshuler D (2014). Loss-of-function mutations in SLC30A8 protect against type 2 diabetes. Nature Genetics 45: 1380-1385.
Chudasama KK, Winnay J, Johansson S, Claudi T, König R, Haldorsen I, Johansson B, Woo JR, Aarskog D, Sagen JV, Kahn CR, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2013). SHORT syndrome with partial lipodystrophy due to impaired phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase signaling. American Journal of Human Genetics 93: 150-157.
Flannick J, Beer NL, Bick AG, Agarwala V, Molnes J, Gupta N, Burtt NP, Florez JC, Meigs JB, Taylor H, Lyssenko V, Irgens H, Fox E, Burslem F, Johansson S, Brosnan MJ, Trimmer JK, Newton-Cheh C, Tuomi T, Molven A, Wilson JG, O’Donnell CJ, Kathiresan S, Hirschhorn JN, Njølstad PR, Rolph T, Seidman JG, Gabriel S, Cox DR, Seidman CE, Groop L & Altshuler D (2013). Assessing the phenotypic effects in the general population of rare variants in genes for a dominant Mendelian form of type 2 diabetes. Nature Genetics 45: 1380-1385.
Irgens HU, Molnes J, Johansson BB, Ringdal M, Skrivarhaug T, Undlien DE, Søvik O, Joner G, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2013). Prevalence of monogenic diabetes in the population-based Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Registry. Diabetologia 56: 1512-1519.
Johansson S, Irgens H, Chudasama KK, Molnes J, Aerts J, Roque FS, Jonassen I, Levy S, Lima K, Knappskog PM, Bell GI, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2012). Exome sequencing and genetic testing for MODY. PLoS ONE 7 (5): e38050.
Negahdar M, Johansson BB, Aukrust I, Molnes J, Molven A, Matschinsky FM, Søvik O, Kulkarni RN, Flatmark T, Njølstad PR & Bjørkhaug L (2012). GCK-MODY diabetes associated with protein misfolding, cellular self-association and degradation. BBA Molecular Basis of Disease 1822: 1705-1715.
Njølstad PR & Molven A (2012). To test, or not to test: time for a MODY calculator? Diabetologia 55: 1231-1234.
Haldorsen IS, Ræder H, Vesterhus M, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2012). The role of pancreatic imaging in monogenic diabetes mellitus. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 8: 148-159.
Søvik O, Aagenæs Ø, Eide SÅ, Mackay D, Temple IK, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2012). Familial occurrence of neonatal diabetes with duplications in chromosome 6q24: treatment with sulfonylurea and 40-yr follow-up. Pediatric Diabetes 13: 155-162.
Gonc EN, Ozturk BB, Haldorsen IS, Molnes J, Immervoll H, Ræder H, Molven A, Søvik O, & Njølstad PR (2012). HNF1B mutation in a Turkish child with renal and exocrine pancreas insufficiency, diabetes and liver disease. Pediatric Diabetes 13: e1-e5.
Molven A & Njølstad PR (2011). Role of molecular genetics in transforming diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics 11: 313-320.
Hertel JK, Johansson S, Ræder H, Platou CGP, Midthjell K, Hveem K, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2011). Evaluation of four novel genetic variants affecting hemoglobin A1c levels in a population-based type 2 cohort (the HUNT2 study). BMC Medical Genetics 12: 20 (1-6).
Hertel JK, Johansson S, Sonestedt E, Jonsson A, Lie RT, Platou CGP, Nilsson PM, Rukh G, Midthjell K, Hveem K, Melander O, Groop L, Lyssenko V, Molven A, Orho-Melander M & Njølstad PR (2011). FTO, type 2 diabetes and weight gain throughout adult life. A meta-analysis of 41,504 subjects from the Scandinavian HUNT, MDC, and MPP studies. Diabetes 60: 1637-1644.
Lango Allen H, Johansson S, Ellard S, Shields B, Hertel JK, Ræder H, Colclough K, Molven A, Frayling TM, Njølstad PR, Hattersley AT & Weedon MN (2010). Polygenic risk variants for type 2 diabetes susceptibility modify age at diagnosis in monogenic HNF1A diabetes. Diabetes 59: 266-271.
Ragvin A, Moro E, Fredman D, Navratilova P, Drivenes Ø, Engström PG, Alonso ME, Mustienes EC, Skarmeta JLG, Tavares MJ, Casares F, Manzanares M, van Heyningen V, Molven A, Njølstad PR Argenton F, Lenhard B & Becker TS (2010). Long-range gene regulation links genomic type 2 diabetes and obesity risk regions to HHEX, SOX4 and IRX3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA107: 775-780.
Laborie LB, Mackay DJG, Temple IK, Molven A, Søvik O & Njølstad PR (2010). DNA hypomethylation, transient neonatal diabetes and prune belly sequence in one of two identical twins. European Journal of Pediatrics 169: 207-213.
Hertel JK, Johansson S, Ræder H, Midthjell K, Lyssenko V, Groop L, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2008). Genetic analysis of recently identified type 2 diabetes loci in 1,638 unselected patients with type 2 diabetes and 1,858 control participants from a Norwegian population-based cohort (the HUNT study). Diabetologia 51: 971-977.
Sagen JV, Bjørkhaug L, Molnes J, Ræder H, Grevle L, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2008). Diagnostic screening of MODY2/GCK mutations in the Norwegian MODY Registry. Pediatric Diabetes 9: 442-449.
Søvik O, Njølstad PR, Jellum E & Molven A (2008). Wolcott-Rallison syndrome with 3-hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria and lethal outcome. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease 31: 547 (#106, 1-5).
Vesterhus M, Haldorsen IS, Ræder H, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2008). Reduced pancreatic volume in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A-maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 93: 3505-3509.
Eide SÅ, Ræder H, Johansson S, Midthjell K, Søvik O, Njølstad PR & Molven A (2008). Prevalence of HNF1A (MODY3) mutations in a Norwegian population (the HUNT2 Study). Diabetic Medicine 25: 775-781.
Haldorsen IS, Vesterhus M, Ræder H, Jensen DK, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2008). Lack of pancreatic body and tail in HNF1B mutation carriers. Diabetic Medicine 25: 782-787.
Molven A, Ringdal M, Nordbø AM, Ræder H, Støy J, Lipkind GM, Steiner DF, Philipson LH, Bergmann I, Aarskog D, Undlien DE, Joner G, Søvik O, the Norwegian Childhood Diabetes Study Group, Bell GI & Njølstad PR (2008). Mutations in the insulin gene can cause MODY and autoantibody-negative type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 57: 1131-1135.
Vesterhus M, Ræder H, Johansson S, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2008). Pancreatic exocrine dysfunction in maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3. Diabetes Care 31: 306-310.
Johansson S, Ræder H, Eide SÅ, Midthjell K, Hveem K, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2007). Studies in 3,523 Norwegians and meta-analysis in 11,571 subjects indicate that variants in the hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4A) P2 region are associated with type 2 diabetes in Scandinavians. Diabetes 56: 3112-3117.
Sagen JV, Odili S, Bjørkhaug L, Zelent D, Buettger C, Kwagh J, Stanley C, Dahl-Jørgensen K,de Beaufort C, Bell GI, Han Y, Grimsby J, Taub R, Molven A, Søvik O, Njølstad PR & Matschinsky FM (2006). From clinicogenetic studies of maturity-onset diabetes of the young to unravelling complex mechanisms of glucokinase regulation. Diabetes 55: 1713-1722.
Ræder H, Bjørkhaug L, Johansson S, Mangseth K, Sagen JV, Hunting A, Følling I, Johansen O, Bjørgaas M, Paus PN, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2006). A hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene (HNF4A) P2 promoter haplotype linked with late-onset diabetes: Studies of HNF4A variants in the Norwegian MODY registry. Diabetes 55: 1899-1903.
Bjørkhaug L, Bratland A, Njølstad PR & Molven A (2005). Functional dissection of the HNF-1-alpha transcription factor: A study on nuclear localization and transcriptional activation. DNA and Cell Biology 24: 661-669.
Bjørkhaug L, Johansson S, Ræder H, Thorsby PM, Undlien DE, Søvik O, Molven A, Sagen JV & Njølstad PR (2005). Molecular diagnostics in diabetes mellitus. Tidsskrift for Den Norske Lægeforening 125: 2968-2972. [in Norwegian]
Njølstad PR, Molven A & Søvik O (2005). Diagnosis and management of MODY in a pediatric setting. Pp. 84-93 in Diabetes in Childhood and Adolescence (Eds. Chiarelli F, Dahl-Jørgensen K & Kiess W). Karger, Basel, Switzerland 2005. ISBN 3-8055-7766-4.
Sagen JV, Baumann ME, Salvesen HB, Molven A, Søvik O & Njølstad PR (2005). Diagnostic screening of NEUROD1 (MODY6) in subjects with MODY or gestational diabetes. Diabetic Medicine 22: 1012-1015.
Sagen JV, Ræder H, Hathout E, Shehadeh N, Gudmundsson K, Bævre H, Abuelo D, Phornphutkul C, Molnes J, Bell GI, Gloyn AL, Hattersley AT, Molven A, Søvik O & Njølstad PR (2004). Permanent neonatal diabetes due to mutations in KCNJ11 encoding Kir6.2: Patient characteristics and initial response to sulfonylurea therapy. Diabetes 53: 2713-2718.
Njølstad PR, Sagen JV, Bjørkhaug L, Odili S, Shehadeh N, Bakry D, Sarici SU, Alpay F, Molnes J, Molven A, Søvik O & Matschinsky FM (2003). Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus caused by glucokinase deficiency: inborn error of the glucose-insulin signaling pathway. Diabetes 52: 2854-2860.
Bjørkhaug L, Sagen JV, Thorsby P, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2003). Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene mutations and diabetes in Norway. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 88: 920-931
Njølstad PR, Søvik O, Cuesta-Muñoz A, Bjørkhaug L, Massa O, Barbetti F, Undlien DE, Shiota C, Magnuson MA, Molven A, Matschinsky FM & Bell GI (2001). Neonatal diabetes mellitus due to complete glucokinase deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 344: 1588-1592.
Bjørkhaug L, Ye H, Horikawa Y, Søvik O, Molven A & Njølstad PR (2000). MODY associated with two novel hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha loss-of-function mutations (P112L and Q466X). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 279: 792-798.
Bjørkhaug L, Søvik O, Bell GI, Njølstad PR & Molven A (2000). A simple test for the high-frequency mutation in the HNF-1alpha/MODY3 gene. Diabetologia 43: 818-819.